AMD Ryzen 7000’s Tiny RDNA2 GPU Overclocked to 3.1 GHz

Based on the Zen 4 microarchitecture, AMD’s latest Ryzen 7000 series processors for desktop feature a tiny RDNA-based graphics processing unit inside the I/O die (IOD). This GPU is hardly intended for gaming, but scatter venture For AMD’s Ryzen 7900 processor, the performance is about 42% better ( video cards). This doesn’t mean that GPUs will suddenly become a viable gaming solution, but at least they will perform better.
AMD’s Ryzen 7000 series ‘Raphael’ desktop CPUs will integrate RDNA 2 based GPUs with 128 stream processors and 2 CUs in IODs. This graphics solution runs up to 2.20 GHz and delivers a compute throughput of around 0.563 FP32 TFLOPS. This is comparable to high-end graphics cards from 2007 (such as the ATI Radeon HD 2900 XT). This is not enough to get a decent framerate in modern games. Still, this GPU can display graphics and play some videos. Furthermore, overclocking is also possible.
However, overclocking an integrated GPU is not an easy task. On the one hand, AMD’s Agesa 1.0.0.4 supports iGPU overclocking, but to get the best possible performance out of this graphics processor, play around with AMD’s Precision Boost Overdrive settings and limit voltage and power. should be raised.
On the other hand, significantly increasing the power budget of the Precision Boost Overdrive will not provide a significant improvement as the integrated GPU is a small low-end graphics solution where performance is not intended. Therefore, it makes more sense to manually increase the VDDCR_SOC and VDDCR_GFX voltages to provide more power to the integrated GPU.
By default, GPUs run at 2.20 GHz at 0.997V, but by increasing the voltage to 1.2V, graphics processors can reach 2949 MHz. A further adjustment of the voltage/frequency curvature to 1.395V can push the GPU frequency up to 3.10 GHz. On the other hand, this increases the SoC power from the default of about 38.5W to 60.7W. This means increased cooling requirements.
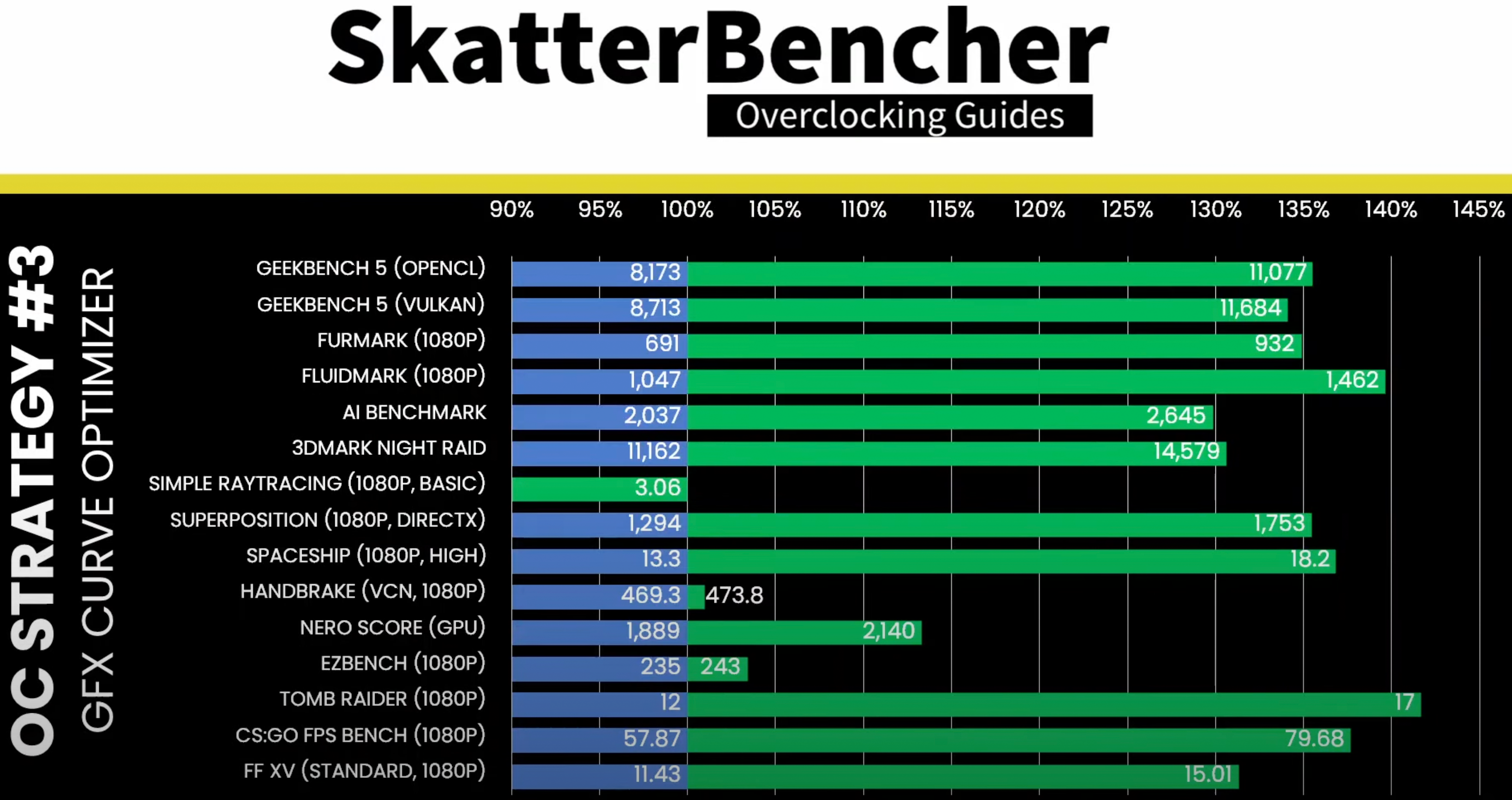
From a performance standpoint, this gives games like Tomb Raider an extra performance of up to 42.5%, but at 17 frames per second, the title remains unplayable. Additionally, you can run raytracing benchmarks that don’t work by default on embedded GPUs. But even such extreme overclocking doesn’t yield substantial performance improvements in many synthetic benchmarks, presumably due to other limitations.
Overclocking an integrated RDNA 2-based GPU doesn’t look like it will yield any real results, but it is doable. Additionally, overclocking an integrated GPU seems easier than overclocking a discrete GPU, as AMD doesn’t allow adjustments to the voltage/frequency curves of their discrete RDNA 3 graphics cards.




