Chainalysis reports $2B lost in cross-chain bridge hacks

Research with blockchain data platform Chainalysis By 2022, it is estimated that $2 billion has been lost to cross-chain bridge hacks so far.
Chainalysis said in its report that the issue now “represents a significant threat to trust-building in blockchain technology.”
Additionally, researchers say bridge hacking is a favorite of North Korean hackers and is estimated to account for half of the $2 billion stolen so far.
The report comes on the heels of the Nomad Bridge hack, where $191 million was stolen. Nomad links the Ethereum, Avalanche, Evmos, Moonbeam, and Milkomeda blockchains.
Cross-chain bridge has multiple vulnerabilities
Cross-chain bridges connect different blockchains and allow data and tokens to be transferred between incompatible chains. This technology is part of the push to make the entire crypto ecosystem interoperable.
Bridges allow you to use assets on another blockchain without leaving the chain and exchanging the required tokens on an exchange. It typically operates through an asset conversion process using a lock-mint-burn mechanism.
However, bridges are susceptible to several Vulnerabilitysingle point of failure/centralization, low liquidity due to the need for centralized entities to hold pools of assets, technical limitations due to lock-mint-burn mechanisms governed by smart contracts Including vulnerabilities, and censorship.
Chain analysis recommendations
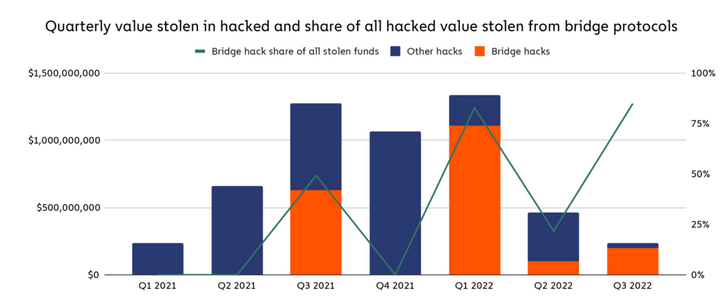
Chainalysis reports that there have been 13 bridge hacks so far this year, accounting for 69% of all stolen funds.
The researchers charted a breakdown of other hacks and bridge hacks that showed no discernible pattern. Bridge hacking didn’t exist until Q3 2021. However, the first quarter of 2022 saw a peak in stolen funds from the bridge. This coincided with a peak in total stolen funds.
Chainalysis said in a report that exchanges used to be a prime target for hackers. However, increased security on exchanges has forced hackers to look for newer and more vulnerable targets.
To combat this problem, researchers sought rigorous smart contract code audits and proven contracts used as templates for developers to build. Chainalysis also advises on “human carelessness” in the report, saying the team needs training to spot “sophisticated social engineering tactics.”
Although no names were mentioned in the report, the above comment was about a Ronin bridge hack that cost Axie Infinity users $615 million, which the platform later refunded.
Recently it became clear that roninbashi hack North Korean hackers staged a targeting of a senior engineer holding a fake job. The process involved fake interviews culminating in job postings sent via infected files . Upon opening the file, the hacker was able to take over control of his nodes on multiple networks.




