Ethereum’s move to PoS is trading off decentralization for scalability


Once the merge is finally complete, Ethereum will run as a Proof of Stake (PoS) network.
However, the move away from Proof-of-Work (PoW) systems is highly controversial. Proponents of PoW mining feared that staking would centralize the network and threaten its independence. Those fighting for PoS networks touted the scalability and accuracy resulting from the new system.
On-chain analysis gives you a clear picture of all the strengths and weaknesses of Merge. A look at the Ethereum blockchain tells us when the transition from PoW to PoS occurred. Mining ETH has become difficult and the hash rate has dropped to zero.
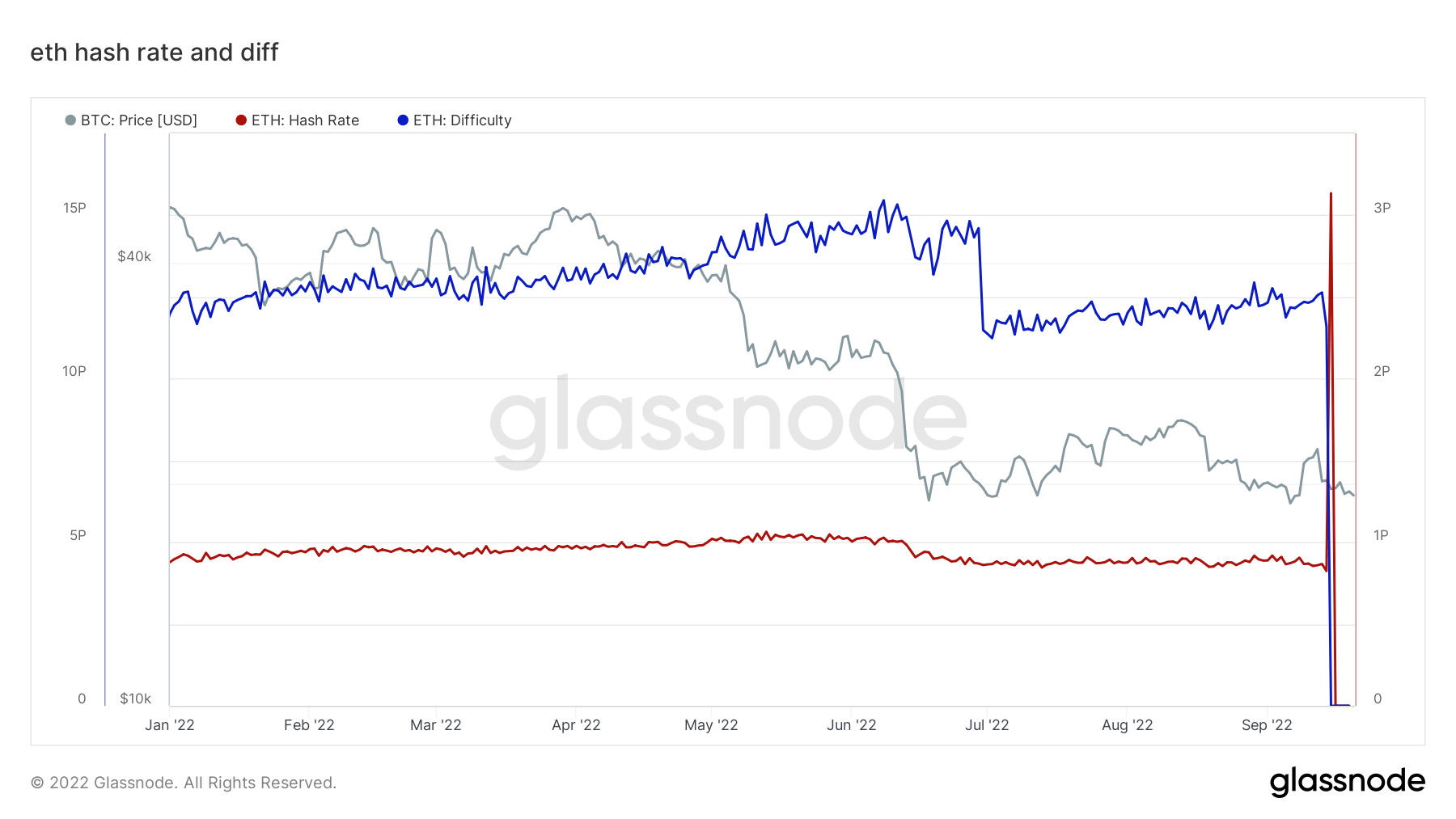
The centralization issues that PoS opponents have warned about are evident on-chain.
Total amount of ETH transferred to ETH2 Deposit contract It currently stands at around 13.8 million ETH via staking providers. About 70% of that amount, or about 10 million ETH, is concentrated in his four staking service providers: Lido, Coinbase, Kraken and Binance.

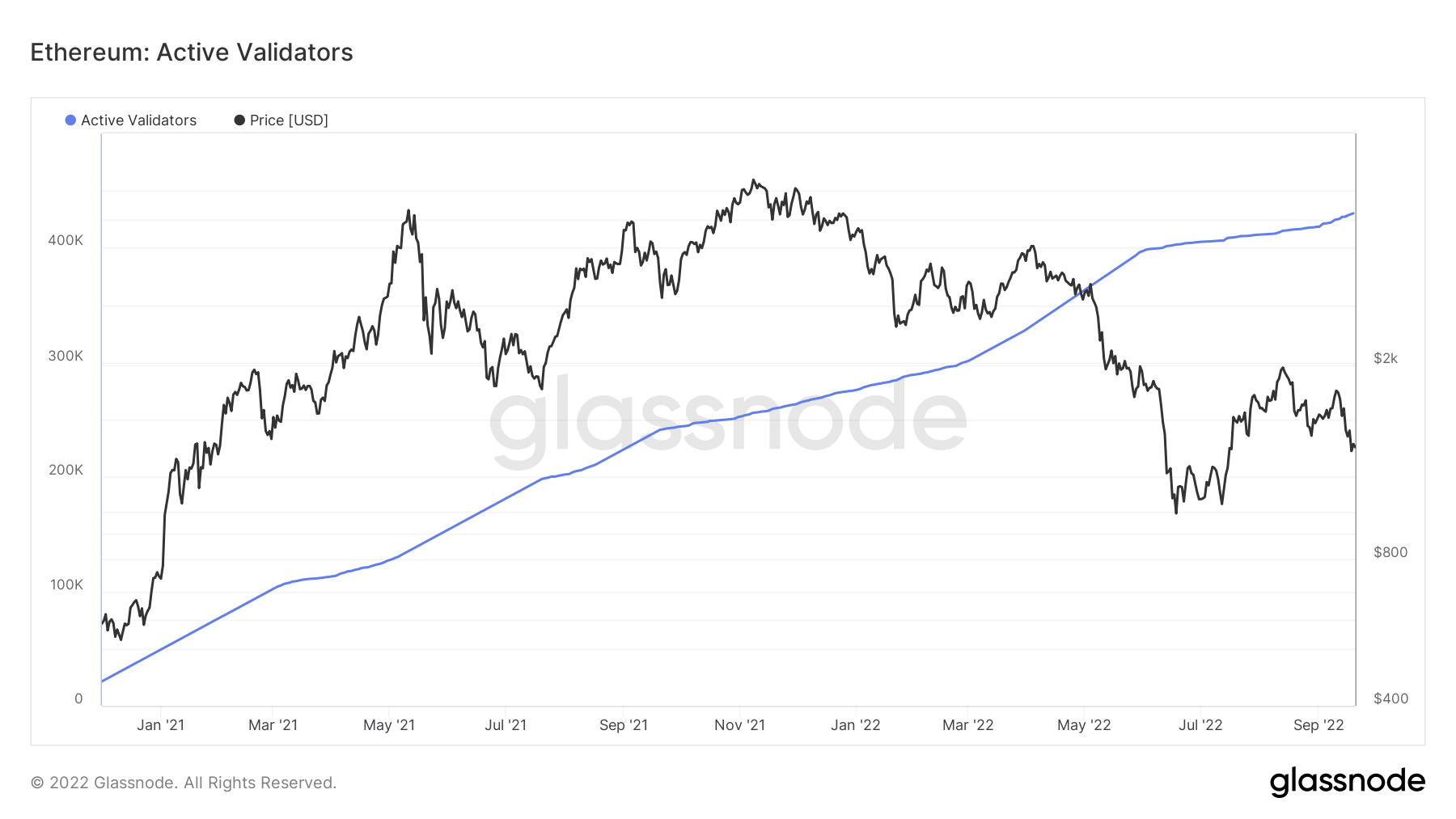
However, the number of active validators on the network has reached an all-time high. Increasing the number of independent validators dramatically increases the decentralization of the network, offering a more aggressive alternative to the centralization found in staking providers.
Active validators are defined as validators who have completed activation, are not in the exit queue, and have an active balance greater than 32 ETH. We currently have over 430,000 active validators, a number that has grown significantly since the merge was announced in January 2021.
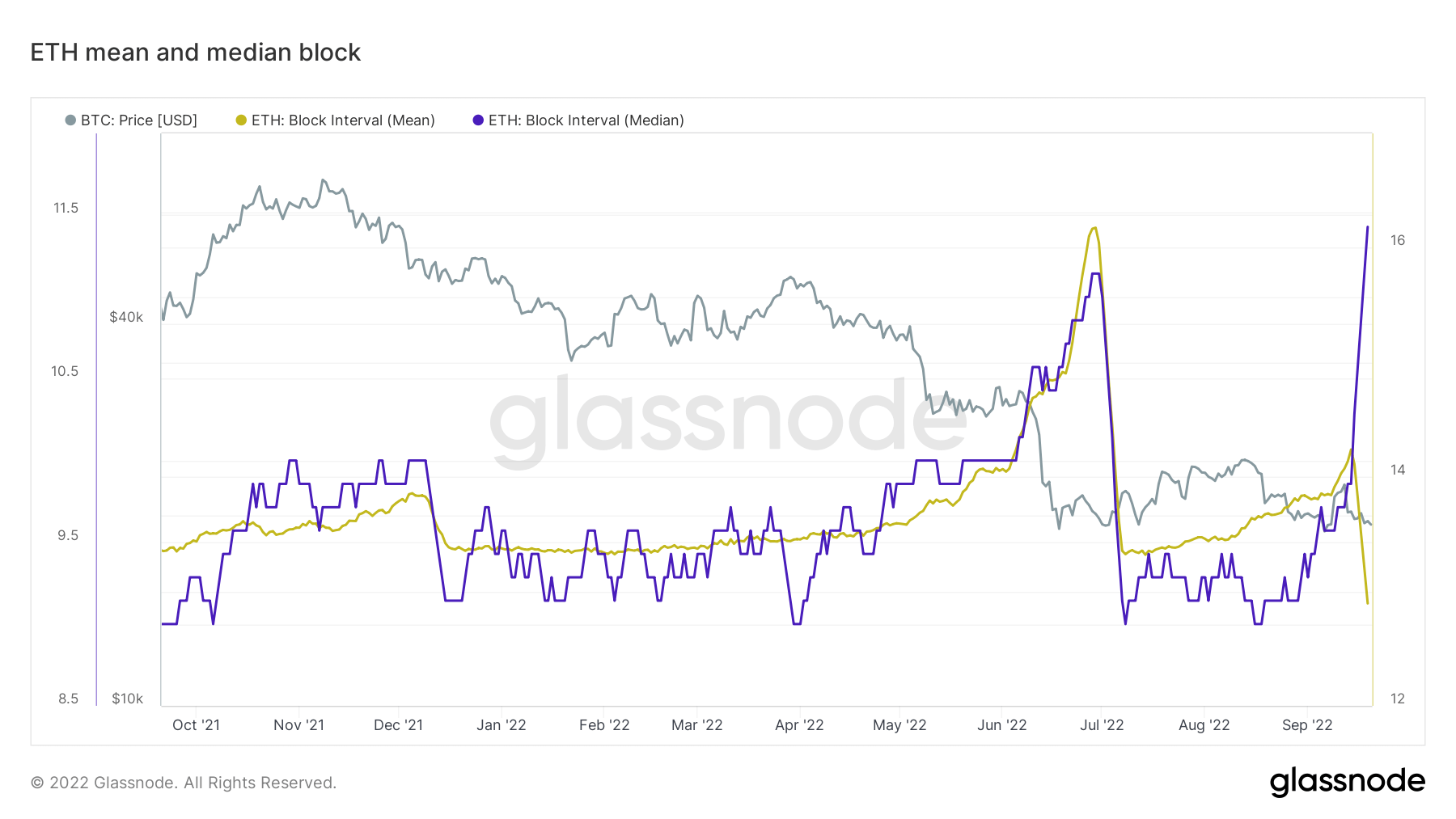
Another tangible advantage that PoS brings to Ethereum is scalability.
15% more block space per day with newly implemented deterministic block time. The move from PoW to PoS reduced the block time from 13.5s to 12s, resulting in an accurate staking consensus. Immediately after the merge, the median time between blocks and the average programmed time decreased to 12 seconds.