How To Monitor Temperature With a Raspberry Pi Pico

of raspberry pi pico An ideal way to get into microcontrollers. Boards start at $4 and are cheap and easy to use. Low cost and ease of use means you can easily drop it into your project without fear of the worst of your wallet.
This how-to uses a Raspberry Pi Pico to capture live temperature data using the DS18B20. These sensors come in many forms, from bare transistor chips to waterproof cables. We use the latter version, which can be partially submerged in liquid to monitor temperature. Our project reads the temperature and uses a conditional test in MicroPython to trigger a blinking LED when the temperature drops below 20 degrees Celsius.
What you need for this project
circuit construction
The circuit consists of two parts. DS18B20 temperature sensor and LED. He divides them into two sections.
The DS18B20 has three connections to the Raspberry Pi Pico.
| raspberry pi pico | wire color | DS18B20 |
|---|---|---|
| 3V3 | Red | VDD |
| GPIO26 | yellow | data |
| earth | black | earth |
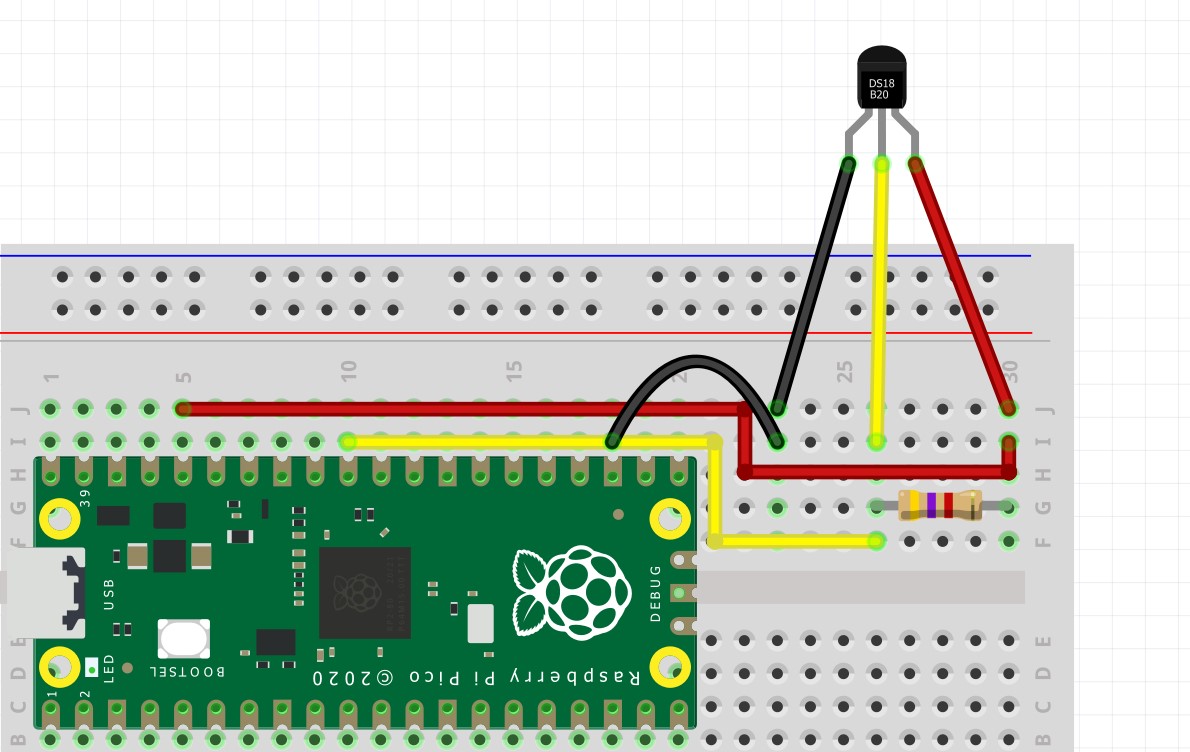
All three connections are made on the breadboard and wires are used to connect to the Pico. There is 4.7K ohms between the data and the 3V3 pins (yellow and red). Resistor This is used to pull the data pin high using the supplied 3.3V. This maintains a stable connection between the data pins and the Pico.
The LED has only two connections to the Raspberry Pi Pico.
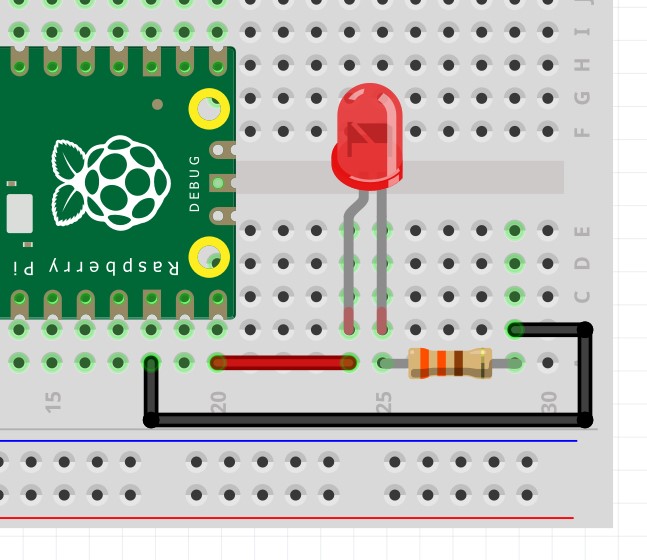
| raspberry pi pico | wire color | lead |
|---|---|---|
| GPIO15 | Red | Anode (long leg) |
| earth | black | Cathode (short leg) |
The cathode leg of the LED has a 330 ohm resistor in line with GND. This reduces the amount of current the LED can consume.
write code
1. follow this guide Download and install the latest MicroPython release for your model of Raspberry Pi Pico. Follow the steps to connect Raspberry Pi Pico to Thonny.
2. Create a new empty project in Thonny.
3. Import three modules of pre-written code. The first is onewire, a module that allows the Pico to communicate with the DS18B20’s single-wire interface. Next is ds18x20. This is the module that interprets the sensor data from the DS18B20 and provides human readable data. Finally, import the time used to pace the project code.
import onewire, ds18x20, timeFour. Import the Pin class from the Machine module. This allows your code to interact with components connected to GPIOs.
from machine import PinFive. Create two objects: SensorPin and alert. SensorPin is the GPIO pin used to connect the data pin from the DS18B20 to the Pico. Alert is a GPIO pin that connects to the anode (long leg) of the LED.
SensorPin = Pin(26, Pin.IN)
alert = Pin(15, Pin.OUT)6. Create an object, Sensor, and use it to tell the ds18x20 module where to find the DS18B20 temperature sensor. This line also uses the onewire module, the protocol that sensors use to connect.
sensor = ds18x20.DS18X20(onewire.OneWire(SensorPin))7. Create an object ROM and use the sensor object to scan the interface and find the DS18B20 temperature sensor. All 1-wire devices such as our DS18B20 have a unique registration number stored in ROM that must be identified prior to use.
roms = sensor.scan()8. Use a while True loop Run the following lines of code in a never-ending loop.
while True:9. Set the temperature reading to use Celsius. Note that the code inside the while True loop is indented to indicate that it belongs to the loop.
sensor.convert_temp()Ten. Add a 2 second pause to your code. This gives the DS18B20 time to stabilize before taking a read.
time.sleep(2)11. Use a for loop to iterate through the returned list of ROMs. There is only one DS18B20 in the 1-wire interface, so the list iterates through contains only one ROM.
for rom in roms:12. Create an object, temperature, and use it to store the reading output of the DS18B20 sensor. The output is wrapped in a round() function which rounds the returned data to one decimal place.
temperature = round(sensor.read_temp(rom),1)13. Use a conditional test to check the value stored in the temperature object against a hardcoded value. In this example, if the temperature is less than or equal to 20 degrees Celsius, the condition evaluates to True and the next section of indented code is executed.
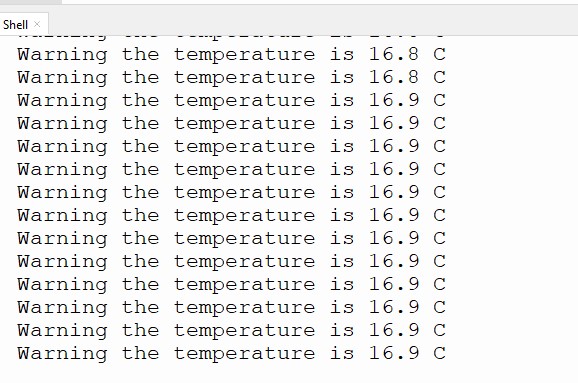
if temperature <= 20:14. Print a message to the Python shell warning the user that the temperature is below 20 C, and include the temperature value in the sentence.
print("Warning the temperature is",temperature,"C")15. Use a for loop to blink the LED 10 times with a 0.5 second delay.
for i in range(10):
alert.toggle()
time.sleep(0.5)16. Create an else condition that activates if the temperature exceeds 20CThis condition outputs the current temperature before exiting.
else:
print(temperature,"C")17. Add a 5 second pause before exiting the loop and returning to the beginning of the loop.
time.sleep(5)18. Save the code on your Raspberry Pi Pico as TemperatureMonitor.py.
19. Click the run icon to start the code. After a few moments, the temperature details will be displayed in the Python shell. If the temperature drops below 20°C, the LED will flash 5 times to warn you.
full code listing
import onewire, ds18x20, time
from machine import Pin
SensorPin = Pin(26, Pin.IN)
alert = Pin(15, Pin.OUT)
sensor = ds18x20.DS18X20(onewire.OneWire(SensorPin))
roms = sensor.scan()
print(roms)
while True:
sensor.convert_temp()
time.sleep(2)
for rom in roms:
temperature = round(sensor.read_temp(rom),1)
if temperature <= 20:
print("Warning the temperature is",temperature,"C")
for i in range(10):
alert.toggle()
time.sleep(0.5)
else:
print(temperature,"C")
time.sleep(5)



